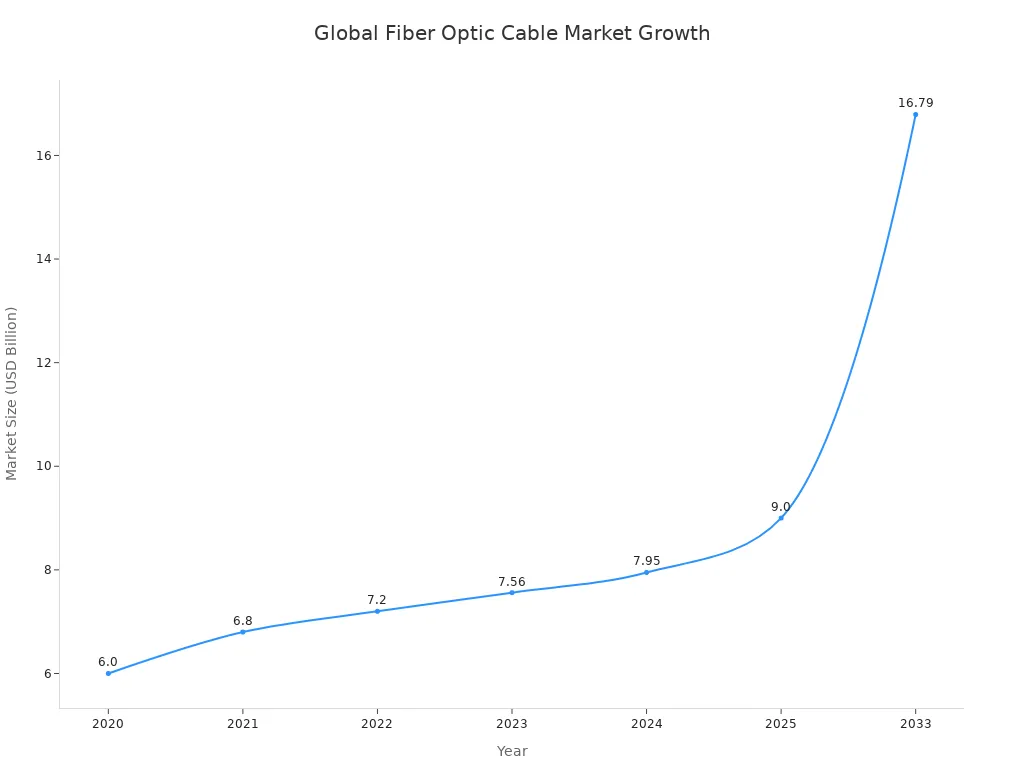
You are important in making fiber optic cables when you know about preform fabrication. This step helps decide how good and strong the final optical fiber will be. Technologies like MCVD, OVD, VAD, and PCVD each change how the cables are made. OVD makes very good glass, and VAD is fast and has low attenuation. You can make more fiber and get the same results every time by learning preform fabrication methods. The world market for fiber optic cable making was $7.24 billion in 2024. It will grow to $16.79 billion by 2033.
New ideas in preform fabrication help start new trends and uses in many industries.
Key Takeaways
- Learning how preform fabrication works is important for making good optical fibers. It affects how strong and clear the fibers are.
- Get to know the four main fabrication technologies: MCVD, OVD, VAD, and PCVD. Each method has special benefits for different needs.
- Use very pure raw materials during fabrication. This helps make fibers that are strong and work well. It also meets what the industry expects.
- Use strict quality checks during shaping and testing. This finds and fixes problems early. It makes sure the fibers work well.
- Keep learning about new ideas in preform fabrication. New technology can make production faster and fibers better. This helps your business stay ahead.
Fiber Preforms Overview

What Is a Preform?
To make fiber optic cables, you need to know about fiber preforms. A preform is a solid rod made of glass or plastic. It is the first step in making optical fiber. The shape and purity of the preform are very important. They decide how the fiber will work. The way a preform looks and its refractive index profile affect the fiber's strength and how it carries light. If the preform is round, you get regular communication fibers. If it is not round, you can make double-clad fibers for lasers. The surface of the preform must be smooth. Any flaw can make the fiber work worse.
There are different kinds of fiber preforms in the industry. Each kind is used for a special job in making fiber.
|
Type of Fiber Preform |
Material |
Application |
|---|---|---|
|
Silica |
Silica |
Telecommunication fibers |
|
Plastic |
Plastic |
Applications needing lower temperatures |
You can also find fiber preforms made from:
- Glass
- Carbon
- Aramid (Kevlar)
- Hybrid materials
These materials help you make fiber preforms for many needs.
Role in Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturing
Fiber preforms are very important in making fiber optic cables. You start with a preform. You heat it and pull it into thin fiber. How good the preform is will change how strong and clear the fiber is. It also affects how well the fiber sends signals. If you want the best fiber, you must use pure and well-made preforms. The right preform helps you get good results every time.
Fiber preforms let you control how the fiber works. The design of the preform lets you change the core and cladding. This changes how light moves inside the fiber. This is needed for things like fast internet, medical tools, and sensors. Using better fiber preforms makes your cables work better and last longer. This helps you keep up with the need for faster and stronger networks.
Preform Fabrication Technologies
You need to know the main fabrication technologies to pick the best way to make optical fiber preforms. Each method changes how good, strong, and repeatable the fiber is. The most used preform fabrication methods are MCVD, OVD, VAD, and PCVD. These vapor deposition methods help you get the right properties for different uses.
MCVD Process
MCVD means Modified Chemical Vapor Deposition. You use this process to make high-quality silica preforms for telecommunication fibers. MCVD is the main technology for making standard fiber preforms. First, you clean a quartz tube with deionized water and acid. Then, you put the tube on a lathe and make it straight with a burner. You use a flame to polish the tube's surface. Chemical bubblers help control the temperature and flow during vapor deposition.
MCVD Process Steps:
- Clean the quartz tube with deionized water and acid.
- Put the tube on the lathe and check if it is straight.
- Use a burner to make the tube straight and remove stress.
- Polish the tube with a hot flame.
- Set up chemical bubblers for steady vapor deposition.
MCVD gives you great gas flow control. This helps you get the right doping and layer features. You get even layers, so the fiber quality stays the same. Automatic testing systems help you keep results steady. Modern process monitoring lets you use complex recipes for making preforms. MCVD helps you get more preforms and supports making standard fiber preforms for telecom networks.
|
Feature |
Advantage |
|---|---|
|
Advanced Gas Flow Control |
Accurate doping and layer characteristics |
|
Exceptional Layer Uniformity |
Impeccable quality and consistency |
|
Automatic Testing Systems |
Consistent and high-quality fiber production |
Tip: MCVD is the top process for making silica optical fibers used in fast communication networks.
OVD Process
OVD means Outside Vapor Deposition. You use this process to make big preforms for mass production. OVD is common for making standard fiber preforms in telecommunications and data systems. You make silica and doped silica particles in a methane-oxygen flame. The soot preform is treated with a drying agent to take out impurities. You dry the preform at high heat to make it more pure. Sintering turns the soot into a solid glass blank.
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Soot-deposition |
Silica and doped silica particles form in a flame by hydrolysis reaction |
|
Preform treatment |
Drying agent takes out impurities |
|
Drying process |
High heat makes the preform more pure |
|
Sintering |
Soot preforms turn into glass blanks through surface energy–driven flow |
With OVD, you can make lots of fiber and get even layers. The process is good for mass production and gives fibers with low signal loss. OVD is growing in the market because it is flexible and can make high-quality optical fibers.
Optical fibers made with OVD are important for telecommunications.
You use them in data systems for steady performance.
VAD Process
VAD means Vapor Axial Deposition. You use this process to make lots of optical fiber preforms quickly. VAD is the best choice for making standard fiber preforms when you want low attenuation and great transmission. You spray raw gases like SiCl4 and GeCl4 from a burner with argon. Flame hydrolysis makes tiny glass powder at high heat. You make the loose powder solid to form a clear glass rod.
VAD Process Steps:
Deposition: Spray raw materials and make glass powder with flame hydrolysis.
- Dehydrated Sintering: Make the powder solid to form a glass rod.
- VAD is good for making many preforms. You get high-quality preforms with low signal loss. VAD had the biggest market share in 2024 because it helps make lots of fiber and gives great transmission. You use VAD for optical fibers in telecom and special uses.
- VAD is used for making lots of high-quality preforms.
- You get low attenuation and steady transmission.
PCVD Process
PCVD means Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition. You use this process to control the refractive index and layer purity very well. PCVD is great for special optical fibers and unique uses. The process lets you make thin layers and very pure layers. You can change fiber profiles for better performance. PCVD uses over 95% of the material, so you get more fiber and less waste.
|
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Precision in Refractive Index |
Makes fibers with special and complex optical features |
|
Fine-layer Deposition |
Lets you shape fiber profiles for advanced uses |
|
Ultra-pure Layer Deposition |
Fewer defects and impurities, so performance and reliability are better |
|
Material Utilization Efficiency |
Over 95% collection efficiency, more fiber, less waste |
|
Layer Deposition Speed |
Fast plasma makes hundreds of layers quickly |
|
Chemical Reaction Efficiency |
Good reaction and deposition of GeO2 and SiO2 |
You pick PCVD for submarine cables and quantum optics. The process gives great optical performance and less risk of contamination. PCVD is the best when you need fibers with complex optical features and high reliability.
- PCVD is used for special optical fibers in advanced uses.
- You get better layer evenness and great performance.
Comparing Preform Fabrication Technologies
You need to look at the main vapor deposition methods to pick the best one for your needs. MCVD is the top choice for silica telecom fiber because it is repeatable and high quality. OVD and VAD are best for making lots of fiber. PCVD is best for precision and purity in special fibers.
|
Technology |
Process Strengths |
Fiber Properties |
Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
|
MCVD |
High reproducibility, uniformity |
Consistent, high quality |
Telecom, standard optical fibers |
|
OVD |
Scalability, flexibility |
Low signal loss |
Data transmission, telecom |
|
VAD |
Mass production, low attenuation |
Excellent transmission |
Telecom, specialty optical fibers |
|
PCVD |
Precision, purity, efficiency |
Complex optical profiles |
Submarine cables, quantum optics |
Note: You should pick the fabrication process based on what you need, the fiber properties you want, and how much you want to make.
Preform Fabrication Process

Raw Material Preparation
You begin by getting the raw materials ready. The materials must be very pure. This is important for making good fiber. If the materials are not pure, the fiber will not work well. You need to pick chemicals that are almost completely pure. For silica-based preforms, you use silicon tetrachloride, germanium tetrachloride, oxygen, and carrier gases. Each one must be very clean. If they are not, the fiber can have problems.
|
Material |
Purity Requirement |
Key Contaminants |
|---|---|---|
|
SiCl4 |
>99.999% |
H2O, Fe, Cu, Cr |
|
GeCl4 |
>99.99% |
H2O, Metal ions |
|
O2 |
>99.95% |
H2O, Hydrocarbons |
|
Carrier gases |
>99.999% |
H2O, O2, Hydrocarbons |
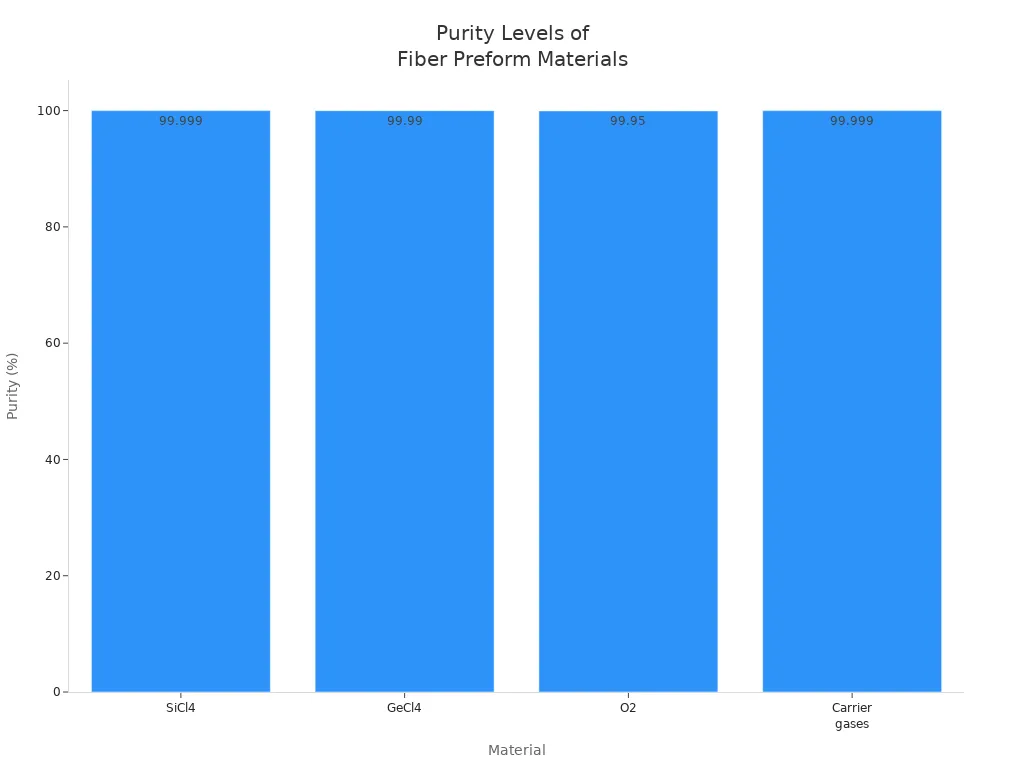
You must take out all dirt and bad stuff before you start. This helps make the fiber strong and clear. Using pure materials stops problems and helps you meet the rules for making fiber. You get better strength and see-through glass. This is needed for fast networks and medical tools.
Deposition
In this step, you add layers to make the core and cladding. The way you do this changes how even the layers are. It also changes how good the fiber is. You can use different ways like Isothermal Chemical Vapor Infiltration, mono-seam, or oscillatory deposition. Each way is good for different jobs.
|
Deposition Technique |
Impact on Layer Uniformity |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
Isothermal Chemical Vapor Infiltration (ICVI) |
Affects uniformity based on preform structure and porosity |
Variations in preform structure influence design options for deposition uniformity and processing time. |
|
Mono-seam Strategy |
Suitable for thin walls |
Follows the medial axis of the wall. |
|
Oscillatory Strategy |
Suitable for thicker walls |
Combines weaving movement in the perpendicular direction. |
|
Deposition Strategy |
Description |
Application |
|---|---|---|
|
Mono-seam Strategy |
Follows the medial axis for thin walls |
Used for thin-walled structures. |
|
Oscillatory Strategy |
Combines weaving movement with medial axis |
Used for thicker walls, enhancing layer uniformity. |
You must watch some important things during this step. These include tube pressure, burner settings, gas flow, and temperature. You use special tools to keep the preform round and the same size. This is very important for the next steps.
|
Parameter |
Importance |
|---|---|
|
Internal Tube Pressure |
Critical for maintaining circularity of the preform; loss of control can lead to distortion. |
|
H2/O2 Burner Ratio |
Affects pressure and glass vaporization rate; optimizing is essential for consistent diameter. |
|
Leak-tight Gas Deposition |
Ensures reliable gas delivery and control over deposition conditions. |
|
Temperature Control (PID) |
Essential for consistency and reproducibility along the preform length. |
You make these steps better to fit what you need. This helps you make preforms that are strong and clear. You can change how you add layers for different uses like internet, medicine, or sensors.
Sintering and Consolidation
Sintering and consolidation turn the layers into a solid glass rod. You use high heat to stick the powder together and fill in holes. This step is needed to make the rod strong and dense for the next step.
Viscous sintering is seen with electron microscopes. It helps join thin powder layers in optical fibers. The speed of this step depends on the capillary number. Sintering changes the inside look and strength of the final product.
During sintering, powder pieces come together to make a solid. The way this happens can change with different materials and heat. Additives can help make the rod denser and stronger. They lower the number of holes in the rod.
You must watch the heat and air around the rod very closely. The sintering heat changes how dense and strong the rod is. You get a denser rod if you use hydrogen instead of a vacuum. The rod shrinks at different rates depending on the heat. Cooling can make the rod grow because of changes inside. You need clean air to stop rust and get the right rod properties. You make these steps better to get strong and clear fiber.
The sintering heat changes how dense and strong the rod is.
- You get a denser rod with hydrogen than with a vacuum.
- The rod shrinks at different rates with different heats.
- Cooling can make the rod grow because of changes inside.
The air must be very clean, especially with more metals in the rod. You must always check the air to make sure it is right. This helps remove bad oxides, especially when heating. The air must be cleaned fast after taking out any oil. This helps get the best rod for making fiber.
Shaping and Quality Control
You shape the rod to meet size and strength rules. You can use prepregs, dry fibers, thermoplastics, or towpregs. Each way has its own good points for making fiber.
|
Shaping Technique |
Characteristics |
Advantages |
Considerations |
Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Prepregs |
Fibers pre-impregnated with partially cured resin |
Consistent resin content and fiber distribution, Excellent mechanical properties |
Relatively expensive, Require careful storage |
Aerospace parts and high-performance applications |
|
Dry Fibers |
Fibers without resin, often held together with a light binder |
Lower material cost, Easier to store and handle |
Requires a separate infusion process, May have challenges with fiber alignment |
Medium to high volume production |
|
Thermoplastics |
Fibers impregnated with thermoplastic resin |
Can be remelted and reshaped, Excellent chemical resistance |
Require higher processing temperatures |
Applications requiring high toughness |
|
Towpregs |
Tows directly impregnated with resin |
Lower cost, Excellent width and thickness control |
Different handling characteristics |
High-volume production |
|
Quality Control |
Various defects like wrinkling, bridging, gaps, and overlaps can occur |
Advanced Inspection Systems, Layer-by-Layer Quality Check, Adaptive Manufacturing, Predictive Modeling |
Solutions to prevent defects during the AFP process |
Ensuring high-quality fiber preforms |
You check for problems at every step. You use special machines to look for mistakes like lines, burn marks, warping, bubbles, dents, weak spots, and color changes. You change how you work to stop these problems and make sure the fiber is good.
|
Defect Type |
Description |
Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
|
Flow lines |
Wavy patterns on the surface, often near mold gates. |
Adjusting injection speed and temperature. |
|
Burn marks |
Black or rust-colored discoloration on edges or surfaces. |
Controlling material temperature and injection speed. |
|
Warping |
Deformation due to uneven shrinkage during cooling. |
Optimizing cooling rates and mold design. |
|
Vacuum voids |
Trapped air bubbles in the molded component. |
Ensuring proper venting in the mold. |
|
Sink marks |
Recesses in the surface due to inner shrinkage. |
Adjusting packing pressure and cooling time. |
|
Weld lines |
Weak bonding lines where molten material converges. |
Modifying injection flow paths and temperatures. |
|
Jetting |
Deformation from premature solidification of injected material. |
Controlling injection speed and pressure. |
|
Discoloration |
Unintended color variations in the molded part. |
Ensuring consistent material quality and mixing. |
You do a last check for mistakes and test the fiber before drawing it. You use tests to make sure the fiber is strong, clear, and works well. You make sure the fiber passes all tests before selling it.
Tip: You can use computer models and smart machines to make the process better for fast networks, medical tools, and sensors.
You help users by making fiber that is strong and works well. You make each step better to get more good fiber. You use tests and checks to make sure every fiber is high quality.
Technology Comparison

Strengths and Limitations
It is important to know what each preform fabrication technology does well and where it has problems. This helps you make good fiber optic cables. MCVD makes fiber that loses little signal and is very even. But, it works slowly and can cause extra signal loss. OVD is a trusted way to make fiber that works well. Still, it can crack if the glass and other parts expand differently when heated. VAD lets you make fiber that can handle heat because it does not have a hole in the middle. You must be careful with the gases used in VAD. PCVD lets you control how light bends and keeps the layers very pure. This is great for special fiber, but people do not talk much about its problems.
|
Technology |
Strengths |
Limitations |
|---|---|---|
|
MCVD |
Makes fiber with little signal loss and even layers |
Works slowly and can cause extra signal loss |
|
OVD |
Trusted method, makes fiber that works well |
Can crack if glass expands differently |
|
VAD |
Handles heat, no hole in the middle |
Needs careful gas control |
|
PCVD |
Controls light bending, makes very pure layers |
Not many known problems |
Tip: Pick the technology that matches what you need for your fiber optic cables. This helps you get strong and reliable fiber.
Applications
Different jobs use different preform fabrication technologies. Aerospace companies pick ways that make fiber strong for tough places and safe for flying. Car makers use fiber to make cars safer and work better. In hospitals, fiber is used in tools that need to be exact and always work. Building and factory workers use fiber to make special shapes and machines. This helps them build new things and work faster.
- Aerospace: Fiber parts stay strong in tough places and are safe.
- Automotive: Fiber makes cars safer and work better.
- Manufacturing: Fiber helps make tools and machines faster.
- Construction: Fiber lets builders make new shapes and designs.
- Healthcare: Fiber helps doctors use exact tools for patients.
You need to pick the right technology for each job. Think about how the fiber needs to look, how strong it must be, and how much it costs. Using prepregs helps keep the fiber lined up and strong. This is important when you move and use the fiber.
Comparative Table
You can look at the main facts for each technology to help you choose. The table below shows how well each one works, how much it costs, and how good the fiber is.
|
Technology |
Efficiency (%) |
Cost Comparison |
Fiber Performance |
Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MCVD |
N/A |
Standard |
Low signal loss, even layers |
Telecom, regular fiber |
|
OVD |
N/A |
Standard |
Works well |
Data, telecom |
|
VAD |
N/A |
Standard |
Handles heat well |
Telecom, special fiber |
|
PCVD |
N/A |
Costs more for special fiber |
Very pure, exact |
Underwater, quantum optics |
|
VPD |
80 |
Costs less to make |
Makes fiber fast |
Lots of fiber at once |
You should think about how long each step takes, how much fiber you can make, and how much material you use. Making fiber quickly and cheaply helps you meet your goals. Picking the best way makes sure your fiber is good and meets what people want.
Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturing Trends

Innovations in Preform Fabrication
Companies are changing how they make fiber for networks. New ways help you get longer and stronger fiber. These fibers lose less signal. HENGTONG preforms can make fiber over 15,000 km long. This is good for trunk communication. The OVD process uses clean vapors to make pure layers. You get high-quality fiber for telecom. VAD technology lets you make lots of long preforms. The quality stays the same each time. MCVD helps you make special fiber types. Some are used in healthcare and security.
|
Innovation Type |
Description |
Impact on Fiber Performance |
|---|---|---|
|
HENGTONG Preform |
Preforms for fiber over 15,000 km, O.D. 80–200 mm |
Low loss, long-distance trunk communication |
|
OVD Process |
Clean vapor for uniform layer deposition |
High purity, low-loss fiber |
|
VAD Technology |
Mass manufacturing of long, consistent preforms |
Fast, reliable fiber for telecom |
|
MCVD Process |
Specialty fiber with tailored characteristics |
Advanced uses in telecom, healthcare |
VAD segment value was over USD 2.1 billion in 2024. This shows people want more fiber made in bulk. MCVD segment may reach USD 15.5 billion by 2034. This means specialty fiber is very important.
Emerging Materials
New materials change how fiber works. Photonic crystal fibers use tiny designs to guide light. This gives you better control over signals. These fibers have low attenuation and bend easily. They are good for sensors and medical devices. Companies mix silica with polymers or rare-earth elements. This makes fiber for special jobs. Some fibers are used in quantum optics or undersea cables.
- Photonic crystal fibers guide light better and lose less signal.
- Hybrid materials help you change fiber for special uses.
- Specialty fiber is used in medicine, security, and fast data.
Industry Challenges
There are problems when making more advanced fiber. You need special machines for bigger fiber parts. You must keep everything very exact. It costs a lot to start, and you may wait for profits. Additive manufacturing does not work well for nanomaterials. This limits new fiber uses. Printing layers slowly makes it hard to make lots of fiber. Not many materials can be printed, so you cannot do everything with photonic crystal fibers.
Note: You need to solve these problems to meet the need for better fiber in telecom, healthcare, and industry.
You help make fiber optic cables better by picking the right preform fabrication technology. When you make each step work well, the fiber gets stronger and costs less to make. This helps you follow the rules set by the industry. Using the best technology means your fiber works great for every job. If you use automation and AI, you can make fiber faster and keep up with other companies. You should watch for new ideas so your fiber always works its best.
|
Aspect |
Impact on Competitiveness |
|---|---|
|
Efficiency and Precision |
Makes more fiber and saves money |
|
Quality Products |
Better fiber means more money for your company |
|
Demand Fulfillment |
Helps give people the fast internet they want |
|
Automation and AI |
Makes fiber more reliable and brings new ideas |
|
Industry 4.0 Technologies |
Finds mistakes and keeps fiber quality the same |
FAQ
Why does fiber optic preform fabrication matter for cable quality?
Making preforms the right way keeps the fiber pure and strong. This helps cables stay clear and lose less signal. New technologies help you follow tough rules. They make sure cables work well in every job.
Why should you choose MCVD, OVD, VAD, or PCVD for your project?
You pick a method that fits what you need. MCVD makes fiber the same every time. OVD is good for making lots of fiber. VAD helps keep signal loss low. PCVD lets you control special fiber features. Each method helps the fiber work better for its job.
Why do you need high-purity raw materials in preform fabrication?
Using clean chemicals stops problems and keeps signals strong. Pure materials make fiber that is tough and see-through. This is important for fast internet and medical tools that must work well.
Why is quality control important during preform shaping?
Checking for mistakes early helps you fix them fast. Quality control makes sure every fiber is made right. This stops big problems and keeps cables working in phones, hospitals, and factories.
Why do innovations in preform fabrication benefit your business?
Trying new ways to make fiber helps your company grow. New ideas let you make longer and stronger fiber with less waste. This helps you sell more and give better products to people.




